EARTH'S SCIENCE
Volcano
– Cone- shaped hill formed by the extrustion of lava
Formation by Subduction
– plates drift a top a thick layer of molten pyrolithic rocks
Formation by Distension
– Caused by a hotspot which is a region of high volcanic activity not located at any plate boundary
Mantle
- This is where the magma came from
Active Volcano
– has record of eruption may erupt again
-for example Mayon, Taal, Smith, Kanlaon, Iraya
Inactive Volcano
– no record of eruption, will not erupt
-Give of steam & sulphurous vapour, for example Arayat, Sto. Thomas, Mt. Makiling, Mt Banahaw, Mt. Apo, Gagua, Bud Dajo
Volcanic Features
-
Cone
– most striking part of a volcano usually composed of mixtures of lava & shape depending on the type of magma that is ejected by a particular volcano
2. Vent
– Opening through which an eruption takes place
3. Magma Chamber
– large underground pool of liquid rocks found beneath the earth’s crust
4. Crater
– is a basin like depression over a vent at the summit of the cone
5. Caldera
– volcanic expression much larger than the original crater. It is created when a volcano’s summit is blown off by exploding gases
6. Lava
– rock or magma expelled from a volcano during eruption
7. Dikes
– barrier or obstacles in a volcano
8. Sills or Intrusive Sheets
– are solified lava flows that originally forced their way between & parallel to older layers of rocks
9. Condult
– channel or pipe conveying liquid materials such as magma
10. Flank
– the side of volcano
11. Summit
– the highest point or apex of volcano
12. Throat
– entrance of a volcano
13. Ash Cloud or Volcanic Ash
– is composed of pulverized rock & glass created during eruption
14. Volcanic Bombs
– chunks of lava blasted into the air which solidify before reaching the ground
15. Pyroclastic Flow
– fast-moving currents of shot gases & rock travelling downhill from a volcano
16. Tephra Fall
– fragmented material consists of punice, scoula , lithic materials or crystals
17. Lahar & Mudflows
– glowing mixture of volcanic debris & water
Types of Volcanic Eruptions
– volcanoes erupt differently. They are generally classified as wet or dry depending on the magma’s water content. Volcanoes are described according to the style of eruption as follows.
A. Phreatic or Hydrothermal
– is a streamdriven eruption as the hot rocks come in contact with water. It is short lined, characterized by ash columns but may be an onset for of a larger eruption.
B. Phreatomagmatic
– is a violent eruption due to the contact between water & magma. As a result, a large column of very fine ash & high speed & sideway emission of pyroclastics called base surges are observed
C. Strombolian
– a periodic weak to violent eruption characterized by fountain lava
D. Vulcanian
– characterized by tall eruption columns that reach up to20 km high w/ pyroclastic flow & ashfall tephra
E. Plinian
– excessively explosive type of eruption gas & pyroclastics
Shapes of Volcanoes
-
Shield Volcano
– medium, volcanoes in Hawaii, layers
of low viscous lava & quiet volcano.
2. Composite Volcano
– tallest, steep-sided, alternating layers
of pyroclastic materials, secondary vent,
clustered group of vent & violent eruption.
3. Cinder Cones
– smallest, looks like hill, steep &
conica, basalt & single vent.
Factors Affecting Volcanoes Eruptive Style
-
Magma’s Temperature
-
Chemical Composition
-
Amount of Dissolved Gases
-
Hot spring
-
Tourist Spot
-
Gayser
-
Minerals
Less silica content – less viscosity (less viscous)
-
Fluid travels far before solidifying
More silica content – more viscosity (too viscous)
-
Fluid tends to break as it flows
Less amount of gas – more silica (very viscous)
-
Lava doesn’t flow at all as it rises
Less amount of gas – less viscosity
-
Files up at vent resulting a dome
More temperature – less viscosity
-
Lava flows further
More amount of gas – less viscosity
Effects of Volcanoes
-
Soil Fertilizer
-
Source Geothermal Energy
-
Wells are drilled deep into the earth to pump steam or hot water to the surface
-
When the water reaches the surface, the drop in pressure causes the water to turn into steam
-
The steam spins a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity
-
Cooling tower cools the steam which condenses back to water
-
The cooled water is pumped back into the earth is began the process again
Unit 3: Module 2
Climate
– is the general pattern of weather in a certain area over a long period of time
Weather
– is the condition of the atmosphere at a specific place & time
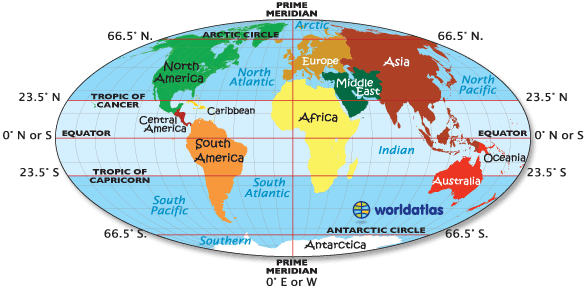
Equator
– is the imaginary line that divides the surface area between north & south pole into two halves
Latitude
– is the distance measured in degrees from the equator to the north or south pole
Altitude
– height above sea level
The earth receives vertical & slanting rays at the same time be of its curved surface
The part that curve away from the sun receive slanting rays
Vertical Rays
– are concentrated on small area , & the slanting rays are spread over a larger area. This is why vertical rays develop more heat than slanting rays.
Bodies of Water
–land/soil absorbs heat factors there water and releases heat factor
Constellation
The Birth of a Star
– star ,dense cloud of gases, hydrogen falls & increase energy
Swollen Star
– Red Giant
Sun Middle aged Star
– Red Giant
Collapsed Star
– white dwarf’
Space
– interstellar dust, temperature is -200 degree celcius, protostar (beginning star)
Stellar Classes
M - Red – 1500-3500 – Betelgluse, Ancares
K – Red to Orange – 3500-5000 – Artoons , Aldebaran
G – Orange to yellow – 6000 – Sun
F – Yellow to White – 7500 – Procyon
A – White – 7500-11000 – Vega
B- Bluest White – 11000-25000 – Rigel
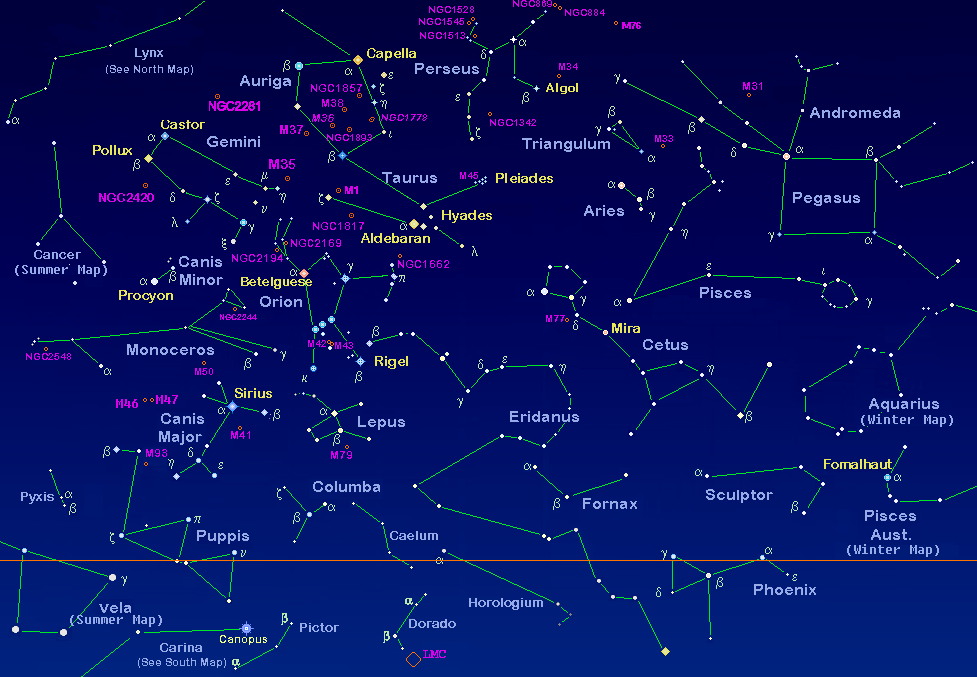
Constellations
– group of stars that forms a pattern
A. Name
-
Animal pattern (shape)
-
Mythological Characters
B. Uses
-
Religion
-
Agriculture
Orion
– winter
Gemini
– summer(april-may)(end of planting season rich harvest)
Pleiades
– January, start of planting
Orion’s Belt
– Tres maria’s, February
Aquila
- Late May , time to clean or clean the fields
Polaris
– North star
Cursa Minor
– little dipper
Stellar Distance
– experienced in light